Important Questions and Answers on Computer Architecture – Part 1
Concepts of computer architecture:
Definatioins:
✓Processor: Active block of the computer that’s responsible for following the
instructions that make up a program. (ex. Intel Core, AMD Ryzen, Apple A-series,
Qualcomm Snapdragon, NVIDIA GeForce, AMD Radeon)
✓ Memory: Memory in computers is a system that encodes, stores, and retrieves data or instructions as bits (0s and 1s).
✓ I/O (Input-Output devices): Any interface or device used to send information into the
computer or to get information out of it.
✓ Bus: Buses are digital connections between functional blocks.
There are two types of buses:
Serial: One bit is transmitted at a time. Usually consists of one wire for data and a few
others for clock and control signals.
Parallel: Several bits are transmitted simultaneously. Usually implemented using several
parallel wires.
Buses are also categorized based on their function:
▪ Data Bus: Carries the actual data being transferred between components (ex,
between the processor and memory).
▪ Address Bus: Carries the memory address specifying where data should be read
from or written to. Ex. the microcontroller uses the address bus to select which
sensor or gauge to read from memory.
▪ Control Bus: Transmits control signals to coordinate operations (e.g., read/write
signals. Ex. the control bus signals the keyboard to send input to the processor
✓ Microprocessors (MPUs): Supported by several external chips that implement
memory, I/O, etc.
✓ Microcontrollers (MCUs): All functionality is contained on a single chip
Von Neumann Architecture:
Non-Von Neumann Harvard Architecture:
Classifications of Computer Architecture (based on how instructions and data are processed, as defined by Flynn's taxonomy)
Introduction to Memory
For example, A computer has a 2 GHz processor:
So, Frequency = 2 GHz
Classification of memory:
Memory Hierarchy & Interfacing
For math:(value of H and T will be given in the question and name of way also mentioned)
way 1: parallel
way 2: sequential
Introduction to Number System:
Convertion
Definations:
What is Digital Logic?
Digital logic is like the building blocks of computer hardware. It’s all about using simple
electronic switches (called logic gates) to work with binary numbers—0s and 1s—to do
calculations, make decisions, or store information.
what is System Design?
System design is like putting together a puzzle using the basic pieces (circuits) created by
digital logic
Key Concepts in Digital Logic
Logic Gates: Logic gates are like tiny decision-makers that take binary inputs (0 or
1) and give a binary output. Each gate does a specific job:
➢ AND: Outputs 1 only if all inputs are 1 (e.g., both A and B are 1).
➢ OR: Outputs 1 if at least one input is 1.
➢ NOT: Flips the input (0 becomes 1, 1 becomes 0).
➢ NAND: Like AND, but the output is flipped.
➢ NOR: Like OR, but the output is flipped.
➢ XOR: Outputs 1 if exactly one input is 1
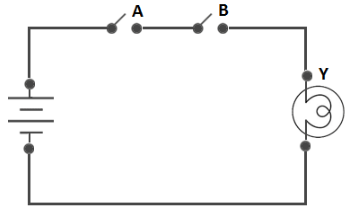
Two-Input AND Gate
The Boolean Expression: Y = 𝑨 . 𝑩 (The value of X will be True when both the inputs
are True)
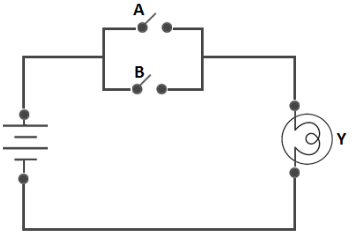
Two-Input OR Gate
The Boolean Expression: 𝐘 = 𝑨 + 𝑩 (The value of X will be high(true) when one of the inputs is set to high (true)).
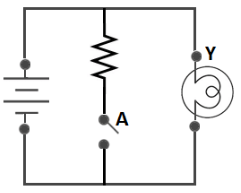
NOT Gate
The Boolean Expression: Y = Ā or Y = A’, the value of Y will be high when A is low
Two-Input NAND Gate
Two Input NOR Gate
The Boolean Expression: Y = (A + B)’ (The value of O will be true when all of its inputs are set
to 0.
The Boolean Expression: Y = (A + B)’ (The value of O will be true when all of its inputs are set
to 0.
Two-Input XOR Gate
Two-Input XNOR Gate
Scenario question for math
Sum-of-Products (SOP): Sum-of-Products (SOP) is a method of writing a logical expression by
adding together ("OR") multiple "AND" groups. Each "AND" group represents a combination of
inputs that makes the output 1, based on a truth table.
Product-of-Sums (POS): Product-of-Sums (POS) is a method of writing a logical expression by
multiplying together ("AND-ing") multiple "OR" groups. Each "OR" group represents a combination of inputs that makes the output 0, based on a truth table.

























No comments